Depth estimation
Depth estimation with event cameras is possible by applying the same approach of disparity calculation on a calibrated stereo camera rig. The straightforward approach is to accumulate frames from events on both cameras and use the same disparity estimation algorithm. This approach might have some limitations, since accumulating events might result in suboptimal results due to low texture available in an accumulated frame.
The dv-processing library provides the dv::camera::StereoGeometry and a few disparity estimation algorithms
that, in combination, can be used to build a depth estimation pipeline.
Semi-dense stereo block matching
Dense block matching here refers to the most straightforward approach: accumulating full frames and running a
conventional disparity estimation on top to estimate depth. Since the accumulated frames only contain limited texture
due to pixels reacting to brightness changes - this approach is referred to as semi-dense. The
SemiDenseStereoMatcher class wraps the disparity estimation part, where estimated disparity can be used to
calculate depth with dv::camera::StereoGeometry.
Following sample code show the use of SemiDenseStereoMatcher with dv::camera::StereoGeometry
to run a real-time depth estimation pipeline on a calibration stereo camera.
1#include <dv-processing/camera/calibration_set.hpp>
2#include <dv-processing/core/stereo_event_stream_slicer.hpp>
3#include <dv-processing/depth/semi_dense_stereo_matcher.hpp>
4#include <dv-processing/io/camera/discovery.hpp>
5#include <dv-processing/noise/background_activity_noise_filter.hpp>
6
7#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
8
9int main() {
10 using namespace std::chrono_literals;
11
12 // Path to a stereo calibration file, replace with a file path on your local file system
13 const std::string calibrationFilePath = "path/to/calibration.json";
14
15 // Load the calibration file
16 auto calibration = dv::camera::CalibrationSet::LoadFromFile(calibrationFilePath);
17
18 // It is expected that calibration file will have "C0" as the leftEventBuffer camera
19 auto leftCameraCalib = calibration.getCameraCalibration("C0").value();
20
21 // The second camera is assumed to be rightEventBuffer-side camera
22 auto rightCameraCalib = calibration.getCameraCalibration("C1").value();
23
24 // Open the stereo camera with camera names from calibration
25 auto leftCamera = dv::io::camera::openSync(leftCameraCalib.name);
26 auto rightCamera = dv::io::camera::openSync(rightCameraCalib.name);
27
28 dv::io::camera::synchronizeAnyTwo(leftCamera, rightCamera);
29
30 // Make sure both cameras support event stream output, throw an error otherwise
31 if (!leftCamera->isEventStreamAvailable() || !rightCamera->isEventStreamAvailable()) {
32 throw dv::exceptions::RuntimeError("Input camera does not provide an event stream.");
33 }
34
35 // Initialize a stereo block matcher with a stereo geometry from calibration and the preconfigured SGBM instance
36 dv::SemiDenseStereoMatcher blockMatcher(
37 std::make_unique<dv::camera::StereoGeometry>(leftCameraCalib, rightCameraCalib));
38
39 // Initialization of a stereo event sliver
40 dv::StereoEventStreamSlicer slicer;
41
42 // Initialize a window to show previews of the output
43 cv::namedWindow("Preview", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
44
45 // Local event buffers to implement overlapping window of events for accumulation
46 dv::EventStore leftEventBuffer, rightEventBuffer;
47
48 // Use one third of the resolution as count of events per accumulated frame
49 const size_t eventCount = static_cast<size_t>(leftCameraCalib.resolution.area()) / 3;
50
51 // Register a callback to be done at 30Hz
52 slicer.doEveryTimeInterval(33ms, [&blockMatcher, &leftEventBuffer, &rightEventBuffer, eventCount](
53 const auto &leftEvents, const auto &rightEvents) {
54 // Push input events into the local buffers
55 leftEventBuffer.add(leftEvents);
56 rightEventBuffer.add(rightEvents);
57
58 // If the number of events is above the count, just keep the latest events
59 if (leftEventBuffer.size() > eventCount) {
60 leftEventBuffer = leftEventBuffer.sliceBack(eventCount);
61 }
62 if (rightEventBuffer.size() > eventCount) {
63 rightEventBuffer = rightEventBuffer.sliceBack(eventCount);
64 }
65
66 // Pass these events into block matcher and estimate disparity, the matcher will accumulate frames
67 // internally. The disparity output is 16-bit integer, that has sub-pixel precision.
68 const auto disparity = blockMatcher.computeDisparity(leftEventBuffer, rightEventBuffer);
69
70 // Convert disparity into 8-bit integers with scaling and normalize the output for a nice preview.
71 // This loses the actual numeric value of the disparity, but it's a nice way to visualize the disparity.
72 cv::Mat disparityU8, disparityColored;
73 disparity.convertTo(disparityU8, CV_8UC1, 1.0 / 16.0);
74 cv::normalize(disparityU8, disparityU8, 0, 255, cv::NORM_MINMAX);
75
76 // Convert the accumulated frames into colored images for preview.
77 std::vector<cv::Mat> images(3);
78 cv::cvtColor(blockMatcher.getLeftFrame().image, images[0], cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
79 cv::cvtColor(blockMatcher.getRightFrame().image, images[1], cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
80
81 // Apply color-mapping to the disparity image, this will encode depth with color: red - close; blue - far.
82 cv::applyColorMap(disparityU8, images[2], cv::COLORMAP_JET);
83
84 // Concatenate images and show them in a window
85 cv::Mat preview;
86 cv::hconcat(images, preview);
87 cv::imshow("Preview", preview);
88 });
89
90 // Buffer input events in these variables to synchronize inputs
91 std::optional<dv::EventStore> leftEvents = std::nullopt;
92 std::optional<dv::EventStore> rightEvents = std::nullopt;
93
94 // Run the processing loop while both cameras are connected
95 while (leftCamera->isRunning() && rightCamera->isRunning()) {
96 // Read events from respective left / right cameras
97 if (!leftEvents.has_value()) {
98 leftEvents = leftCamera->getNextEventBatch();
99 }
100 if (!rightEvents.has_value()) {
101 rightEvents = rightCamera->getNextEventBatch();
102 }
103
104 // Feed the data into the slicer and reset the buffer
105 if (leftEvents && rightEvents) {
106 slicer.accept(*leftEvents, *rightEvents);
107 leftEvents = std::nullopt;
108 rightEvents = std::nullopt;
109 }
110
111 // Wait for a small amount of time to avoid CPU overhaul
112 cv::waitKey(1);
113 }
114
115 return 0;
116}
1from datetime import timedelta
2
3import cv2 as cv
4import dv_processing as dv
5
6# Path to a stereo calibration file, replace with a file path on your local file system
7calibration_file_path = "path/to/calibration.json"
8
9# Load the calibration file
10calibration = dv.camera.CalibrationSet.LoadFromFile(calibration_file_path)
11
12# It is expected that calibration file will have "C0" as the leftEventBuffer camera
13left_camera = calibration.getCameraCalibration("C0")
14
15# The second camera is assumed to be rightEventBuffer-side camera
16right_camera = calibration.getCameraCalibration("C1")
17
18# Open the stereo camera with camera names from calibration
19left_camera_capture = dv.io.camera.openSync(left_camera.name)
20right_camera_capture = dv.io.camera.openSync(right_camera.name)
21
22dv.io.camera.synchronizeAnyTwo(left_camera_capture, right_camera_capture)
23
24# Make sure both cameras support event stream output, throw an error otherwise
25if not left_camera_capture.isEventStreamAvailable() or not right_camera_capture.isEventStreamAvailable():
26 raise RuntimeError("Input camera does not provide an event stream.")
27
28# Initialize a stereo block matcher with a stereo geometry from calibration and the preconfigured SGBM instance
29block_matcher = dv.SemiDenseStereoMatcher(dv.camera.StereoGeometry(left_camera, right_camera))
30
31# Initialization of a stereo event sliver
32slicer = dv.StereoEventStreamSlicer()
33
34# Initialize a window to show previews of the output
35cv.namedWindow("Preview", cv.WINDOW_NORMAL)
36
37# Local event buffers to implement overlapping window of events for accumulation
38global left_event_buffer, right_event_buffer
39left_event_buffer = dv.EventStore()
40right_event_buffer = dv.EventStore()
41
42# Use one third of the resolution as count of events per accumulated frame
43event_count = int((left_camera.resolution[0] * left_camera.resolution[1]) / 3)
44
45
46# Stereo slicer callback method
47def callback(left_events: dv.EventStore, right_events: dv.EventStore):
48 # Push input events into the local buffers
49 global left_event_buffer, right_event_buffer
50 left_event_buffer.add(left_events)
51 right_event_buffer.add(right_events)
52
53 # If the number of events is above the count, just keep the latest events
54 if len(left_event_buffer) > event_count:
55 left_event_buffer = left_event_buffer.sliceBack(event_count)
56 if len(right_event_buffer) > event_count:
57 right_event_buffer = right_event_buffer.sliceBack(event_count)
58
59 # Pass these events into block matcher and estimate disparity, the matcher will accumulate frames
60 # internally. The disparity output is 16-bit integer, that has sub-pixel precision.
61 disparity = block_matcher.computeDisparity(left_event_buffer, right_event_buffer)
62
63 # Convert the accumulated frames into colored images for preview.
64 images = []
65 images.append(cv.cvtColor(block_matcher.getLeftFrame().image, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR))
66 images.append(cv.cvtColor(block_matcher.getRightFrame().image, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR))
67
68 # Convert disparity into 8-bit integers with scaling and normalize the output for a nice preview.
69 # This loses the actual numeric value of the disparity, but it's a nice way to visualize the disparity.
70 # Apply color-mapping to the disparity image, this will encode depth with color: red - close; blue - far.
71 images.append(cv.applyColorMap(cv.normalize(disparity, None, 0, 255, cv.NORM_MINMAX, cv.CV_8UC1), cv.COLORMAP_JET))
72
73 # Concatenate images and show them in a window
74 cv.imshow("Preview", cv.hconcat(images))
75
76
77# Register a callback to be done at 30Hz
78slicer.doEveryTimeInterval(timedelta(milliseconds=33), callback)
79
80# Buffer input events in these variables to synchronize inputs
81left_events = None
82right_events = None
83
84# Run the processing loop while both cameras are connected
85while left_camera_capture.isRunning() and right_camera_capture.isRunning():
86 # Read events from respective left / right cameras
87 if left_events is None:
88 left_events = left_camera_capture.getNextEventBatch()
89 if right_events is None:
90 right_events = right_camera_capture.getNextEventBatch()
91
92 # Feed the data into the slicer and reset the buffer
93 if left_events is not None and right_events is not None:
94 slicer.accept(left_events, right_events)
95 left_events = None
96 right_events = None
97
98 # Wait for a small amount of time to avoid CPU overhaul
99 cv.waitKey(1)

Expected result of semi-dense disparity estimation. The output provides two accumulated frames and color-coded disparity map.
Note
Disparity map yields results only in areas with visible texture, areas without texture contain speckle noise.
Sparse disparity estimation
The semi-dense appraoch is a straightforward to stereo disparity estimation. Another approach is to perform disparity estimation on sparse selected regions within accumulated image. Sparse estimation approach allows the implementation to select regions with enough texture to be selected for the disparity, reducing computational complexity and improving quality. The sparse approach takes point coordinates of where the disparity needs to be estimated, performs sparse accumulation only in the regions where disparity matching actually needs to happen and runs correlation based template matching of left image patches on the right camera image. Each template is matched against the other image on a horizontal line using normalized correlation coefficient (Pearson correlation) and the best scoring match is considered to be the correct match and according disparity is assigned to that point.
The following sample code shows the use of sparse disparity block matcher with a live calibrated stereo camera:
1#include <dv-processing/camera/calibration_set.hpp>
2#include <dv-processing/cluster/mean_shift/event_store_adaptor.hpp>
3#include <dv-processing/core/stereo_event_stream_slicer.hpp>
4#include <dv-processing/data/utilities.hpp>
5#include <dv-processing/depth/sparse_event_block_matcher.hpp>
6#include <dv-processing/io/camera/discovery.hpp>
7#include <dv-processing/visualization/colors.hpp>
8
9#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
10
11int main() {
12 using namespace std::chrono_literals;
13
14 // Path to a stereo calibration file, replace with a file path on your local file system
15 const std::string calibrationFilePath = "path/to/calibration.json";
16
17 // Load the calibration file
18 auto calibration = dv::camera::CalibrationSet::LoadFromFile(calibrationFilePath);
19
20 // It is expected that calibration file will have "C0" as the leftEventBuffer camera
21 auto leftCameraCalib = calibration.getCameraCalibration("C0").value();
22
23 // The second camera is assumed to be rightEventBuffer-side camera
24 auto rightCameraCalib = calibration.getCameraCalibration("C1").value();
25
26 // Open the stereo camera with camera names from calibration
27 auto leftCamera = dv::io::camera::openSync(leftCameraCalib.name);
28 auto rightCamera = dv::io::camera::openSync(rightCameraCalib.name);
29
30 dv::io::camera::synchronizeAnyTwo(leftCamera, rightCamera);
31
32 // Make sure both cameras support event stream output, throw an error otherwise
33 if (!leftCamera->isEventStreamAvailable() || !rightCamera->isEventStreamAvailable()) {
34 throw dv::exceptions::RuntimeError("Input camera does not provide an event stream.");
35 }
36
37 // Matching window size for the block matcher
38 const cv::Size window(24, 24);
39 // Minimum disparity value to measure
40 const int minDisparity = 0;
41 // Maximum disparity value
42 const int maxDisparity = 40;
43 // Minimum z-score value that a valid match can have
44 const float minScore = 0.0f;
45
46 // Initialize the block matcher with rectification
47 auto matcher
48 = dv::SparseEventBlockMatcher(std::make_unique<dv::camera::StereoGeometry>(leftCameraCalib, rightCameraCalib),
49 window, maxDisparity, minDisparity, minScore);
50
51 // Initialization of a stereo event sliver
52 dv::StereoEventStreamSlicer slicer;
53
54 // Initialize a window to show previews of the output
55 cv::namedWindow("Preview", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
56
57 // Local event buffers to implement overlapping window of events for accumulation
58 dv::EventStore leftEventBuffer, rightEventBuffer;
59
60 // Use one third of the resolution as count of events per accumulated frame
61 const size_t eventCount = static_cast<size_t>(leftCameraCalib.resolution.area()) / 3;
62
63 // Register a callback to be done at 50Hz
64 slicer.doEveryTimeInterval(20ms, [&matcher, &leftEventBuffer, &rightEventBuffer, eventCount, &window](
65 const auto &leftEvents, const auto &rightEvents) {
66 // Push input events into the local buffers
67 leftEventBuffer.add(leftEvents);
68 rightEventBuffer.add(rightEvents);
69
70 // If the number of events is above the count, just keep the latest events
71 if (leftEventBuffer.size() > eventCount) {
72 leftEventBuffer = leftEventBuffer.sliceBack(eventCount);
73 }
74 if (rightEventBuffer.size() > eventCount) {
75 rightEventBuffer = rightEventBuffer.sliceBack(eventCount);
76 }
77
78 // Number of clusters to extract
79 constexpr int numClusters = 100;
80
81 // Initialize the mean-shift clustering algorithm
82 dv::cluster::mean_shift::MeanShiftEventStoreAdaptor meanShift(leftEventBuffer, 10.f, 1.0f, 20, numClusters);
83
84 // Find cluster centers which are going to be used for disparity estimation
85 auto centers = meanShift.findClusterCentres<dv::cluster::mean_shift::kernel::Epanechnikov>();
86
87 // Run disparity estimation, the output will contain a disparity estimate for each of the given points.
88 const std::vector<dv::SparseEventBlockMatcher::PixelDisparity> estimates
89 = matcher.computeDisparitySparse(leftEventBuffer, rightEventBuffer, dv::data::convertToCvPoints(centers));
90
91 // Convert the accumulated frames into colored images for preview.
92 std::vector<cv::Mat> images(2);
93 cv::cvtColor(matcher.getLeftFrame().image, images[0], cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
94 cv::cvtColor(matcher.getRightFrame().image, images[1], cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
95
96 // Visualize the matched blocks
97 int32_t index = 0;
98 for (const auto &point : estimates) {
99 // If point estimation is invalid, do not show a preview of it
100 if (!point.valid) {
101 continue;
102 }
103
104 // The rest of the code performs drawing of the match according to the disparity value on the
105 // preview images.
106 const cv::Scalar color = dv::visualization::colors::someNeonColor(index++);
107 // Draw some nice colored markers and rectangles.
108 cv::drawMarker(images[1], *point.matchedPosition, color, cv::MARKER_CROSS, 7);
109 cv::rectangle(images[1],
110 cv::Rect(point.matchedPosition->x - (window.width / 2), point.matchedPosition->y - (window.height / 2),
111 window.width, window.height),
112 color);
113 cv::rectangle(images[0],
114 cv::Rect(point.templatePosition->x - (window.width / 2),
115 point.templatePosition->y - (window.height / 2), window.width, window.height),
116 color);
117 }
118
119 // Concatenate images and show them in a window
120 cv::Mat preview;
121 cv::hconcat(images, preview);
122 cv::imshow("Preview", preview);
123 });
124
125 // Buffer input events in these variables to synchronize inputs
126 std::optional<dv::EventStore> leftEvents = std::nullopt;
127 std::optional<dv::EventStore> rightEvents = std::nullopt;
128
129 // Run the processing loop while both cameras are connected
130 while (leftCamera->isRunning() && rightCamera->isRunning()) {
131 // Read events from respective left / right cameras
132 if (!leftEvents.has_value()) {
133 leftEvents = leftCamera->getNextEventBatch();
134 }
135 if (!rightEvents.has_value()) {
136 rightEvents = rightCamera->getNextEventBatch();
137 }
138
139 // Feed the data into the slicer and reset the buffer
140 if (leftEvents && rightEvents) {
141 slicer.accept(*leftEvents, *rightEvents);
142 leftEvents = std::nullopt;
143 rightEvents = std::nullopt;
144 }
145
146 // Wait for a small amount of time to avoid CPU overhaul
147 cv::waitKey(1);
148 }
149
150 return 0;
151}
1from datetime import timedelta
2
3import cv2 as cv
4import dv_processing as dv
5
6# Path to a stereo calibration file, replace with a file path on your local file system
7calibration_file_path = "path/to/calibration.json"
8
9# Load the calibration file
10calibration = dv.camera.CalibrationSet.LoadFromFile(calibration_file_path)
11
12# It is expected that calibration file will have "C0" as the leftEventBuffer camera
13left_camera = calibration.getCameraCalibration("C0")
14
15# The second camera is assumed to be rightEventBuffer-side camera
16right_camera = calibration.getCameraCalibration("C1")
17
18# Open the stereo camera with camera names from calibration
19left_camera_capture = dv.io.camera.openSync(left_camera.name)
20right_camera_capture = dv.io.camera.openSync(right_camera.name)
21
22dv.io.camera.synchronizeAnyTwo(left_camera_capture, right_camera_capture)
23
24# Make sure both cameras support event stream output, throw an error otherwise
25if not left_camera_capture.isEventStreamAvailable() or not right_camera_capture.isEventStreamAvailable():
26 raise RuntimeError("Input camera does not provide an event stream.")
27
28# Matching window size for the block matcher
29window = (24, 24)
30
31# Minimum disparity value to measure
32min_disparity = 0
33
34# Maximum disparity value
35max_disparity = 40
36
37# Minimum z-score value that a valid match can have
38min_score = 0.0
39
40# Initialize the block matcher with rectification
41matcher = dv.SparseEventBlockMatcher(dv.camera.StereoGeometry(left_camera, right_camera), window, max_disparity,
42 min_disparity, min_score)
43
44# Initialization of a stereo event sliver
45slicer = dv.StereoEventStreamSlicer()
46
47# Initialize a window to show previews of the output
48cv.namedWindow("Preview", cv.WINDOW_NORMAL)
49
50# Local event buffers to implement overlapping window of events for accumulation
51global left_event_buffer, right_event_buffer
52left_event_buffer = dv.EventStore()
53right_event_buffer = dv.EventStore()
54
55# Use one third of the resolution as count of events per accumulated frame
56event_count = int((left_camera.resolution[0] * left_camera.resolution[1]) / 3)
57
58
59# Stereo slicer callback method
60def callback(left_events: dv.EventStore, right_events: dv.EventStore):
61 # Push input events into the local buffers
62 global left_event_buffer, right_event_buffer
63 left_event_buffer.add(left_events)
64 right_event_buffer.add(right_events)
65
66 # If the number of events is above the count, just keep the latest events
67 if len(left_event_buffer) > event_count:
68 left_event_buffer = left_event_buffer.sliceBack(event_count)
69 if len(right_event_buffer) > event_count:
70 right_event_buffer = right_event_buffer.sliceBack(event_count)
71
72 # Number of clusters to extract
73 num_clusters = 100
74
75 # Initialize the mean-shift clustering algorithm
76 mean_shift = dv.cluster.mean_shift.MeanShiftEventStoreAdaptor(left_event_buffer, 10, 1, 20, num_clusters)
77
78 # Find cluster centers which are going to be used for disparity estimation
79 centers = mean_shift.findClusterCentresEpanechnikov()
80
81 # Run disparity estimation, the output will contain a disparity estimate for each of the given points.
82 estimates = matcher.computeDisparitySparse(left_event_buffer, right_event_buffer, list(map(lambda x: x.pt,
83 centers)))
84
85 # Convert the accumulated frames into colored images for preview.
86 images = []
87 images.append(cv.cvtColor(matcher.getLeftFrame().image, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR))
88 images.append(cv.cvtColor(matcher.getRightFrame().image, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR))
89
90 # Visualize the matched blocks
91 index = 0
92 for point in estimates:
93 # If point estimation is invalid, do not show a preview of it
94 if not point.valid:
95 continue
96
97 # The rest of the code performs drawing of the match according to the disparity value on the
98 # preview images.
99 color = dv.visualization.colors.someNeonColor(index)
100 index += 1
101
102 # Draw some nice colored markers and rectangles.
103 cv.drawMarker(images[1], point.matchedPosition, color, cv.MARKER_CROSS, 7)
104 cv.rectangle(images[1],
105 (int(point.matchedPosition[0] - (window[0] / 2)), int(point.matchedPosition[1] - (window[1] / 2))),
106 (int(point.matchedPosition[0] + (window[0] / 2)), int(point.matchedPosition[1] + (window[1] / 2))),
107 color)
108 cv.rectangle(
109 images[0],
110 (int(point.templatePosition[0] - (window[0] / 2)), int(point.templatePosition[1] - (window[1] / 2))),
111 (int(point.templatePosition[0] + (window[0] / 2)), int(point.templatePosition[1] + (window[1] / 2))), color)
112
113 # Concatenate images and show them in a window
114 cv.imshow("Preview", cv.hconcat(images))
115
116
117# Register a callback to be done at 30Hz
118slicer.doEveryTimeInterval(timedelta(milliseconds=33), callback)
119
120# Buffer input events in these variables to synchronize inputs
121left_events = None
122right_events = None
123
124# Run the processing loop while both cameras are connected
125while left_camera_capture.isRunning() and right_camera_capture.isRunning():
126 # Read events from respective left / right cameras
127 if left_events is None:
128 left_events = left_camera_capture.getNextEventBatch()
129 if right_events is None:
130 right_events = right_camera_capture.getNextEventBatch()
131
132 # Feed the data into the slicer and reset the buffer
133 if left_events is not None and right_events is not None:
134 slicer.accept(left_events, right_events)
135 left_events = None
136 right_events = None
137
138 # Wait for a small amount of time to avoid CPU overhaul
139 cv.waitKey(1)
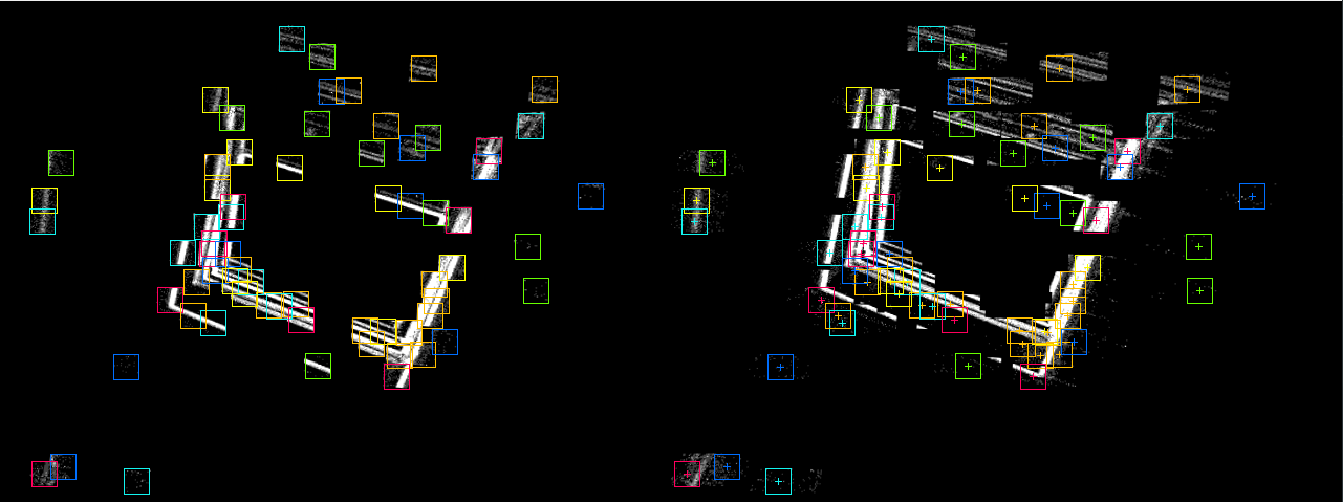
Expected result of sparse disparity estimation. The colored rectangles represent sparse blocks that are matched on the right side image. Block colors are matched on both images. Note that frame are sparse as well - the accumulation happens only in relevant areas around points of interest. The points of interest are selected on high density event areas as per mean-shift cluster extraction.